Synthetic fuels

Synthetic fuels contributing to the realization of a carbon-neutral society
We are working on developing technologies to produce synthetic fuels that can replace existing petroleum products like gasoline, jet fuel, diesel, etc. to achieve carbon neutrality in a wide range of fields, from mobility, such as in aviation, automobiles, and marine transport, to feedstocks for chemicals and lubricants.
Some methods for producing synthetic fuels include processes that use hydrogen, derived from renewable energy, and CO2 as its starting materials or through the gasification of biomass feedstocks. Synthetic fuels can reduce CO2 emissions throughout the entire product lifecycle and thereby contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions in society.
Since synthetic fuels consist of components quite similar to those of existing petroleum products, there is the advantage of being able to use existing refinery equipment, the fuel distribution infrastructure, automobiles, aircraft, etc. already in place. Consequently, if these production technologies are established in the future, synthetic fuels are expected to become one of the options for reducing the overall cost burden on society as we transition toward a carbon-neutral society.
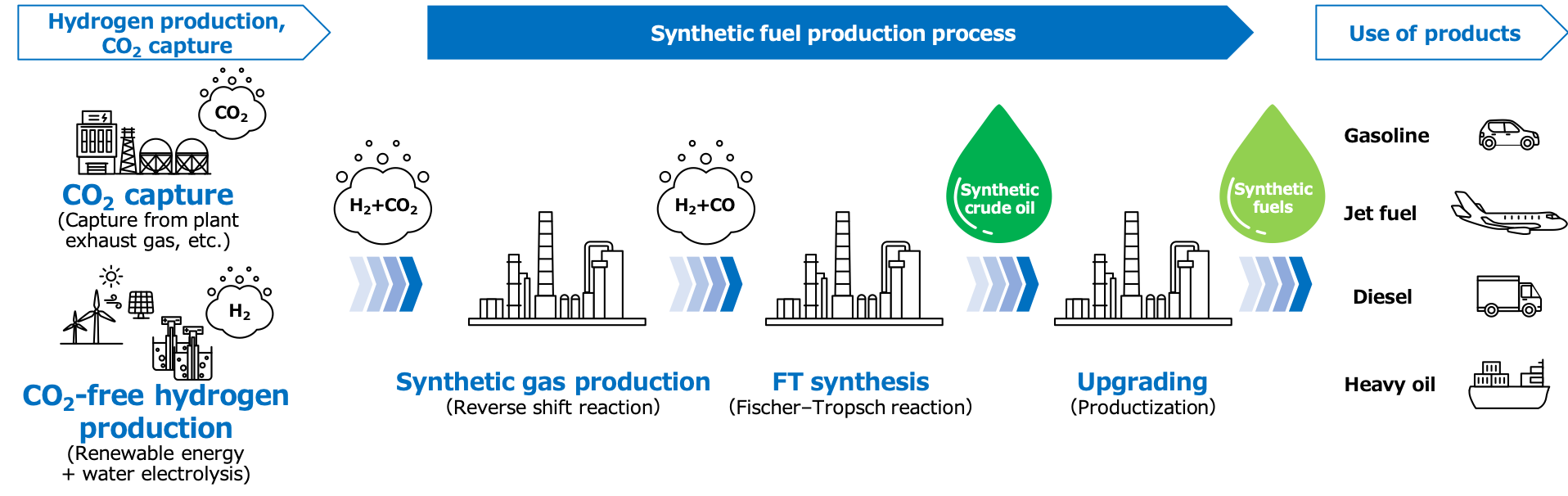
Commercialization of this technology will require a variety of technical innovations such as production process engineering, catalysts technology, etc., so ENEOS is participating in Japan’s New Energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEDO)’s "Green Innovation Fund - Development of Technology for Producing Fuel Using CO2, etc. Project” to establish a technology for highly efficient production process for synthetic fuels.

Catalyst/industrial process developments for producing synthetic fuels with high efficiency
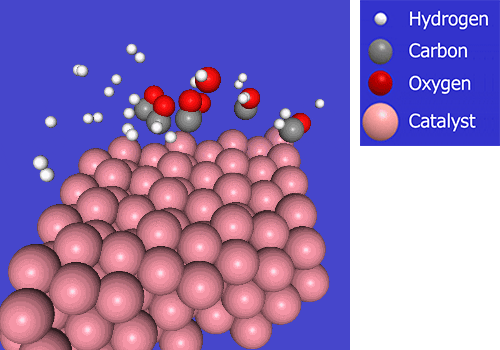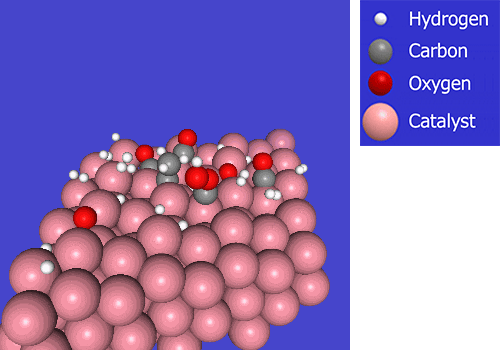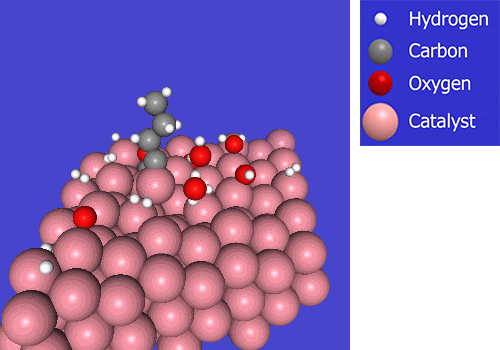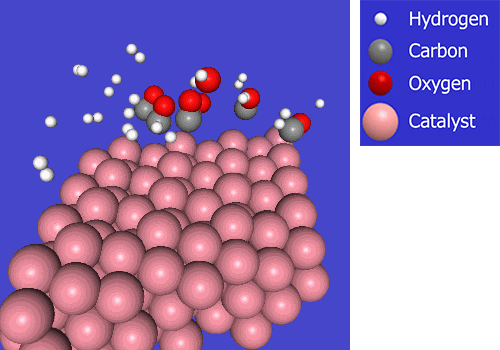
As carbon-neutral fuels, CO2 emissions must be minimized during the synthetic fuels production process. To reduce emissions while lowering costs for broader deployment of synthetic fuels, it is essential to convert feedstocks and input energy into products with minimal losses. When synthesis gas (hydrogen and carbon monoxide) undergoes chemical reactions during production, light gases such as methane are generated as by‑products, leading to losses of feedstock and energy. Consequently, to obtain product in a more efficient manner, it is necessary to develop a catalyst/production process that can minimize these by-products.
In Fischer-Tropsch (FT) synthesis, hydrogen and carbon monoxide (CO) react on a catalyst to produce synthetic crude oil through carbon chain growth. We are working on developing FT catalysts and production processes that can produce synthetic crude oil with high efficiency.
Work toward the commercialization of a Synthetic Fuel production process
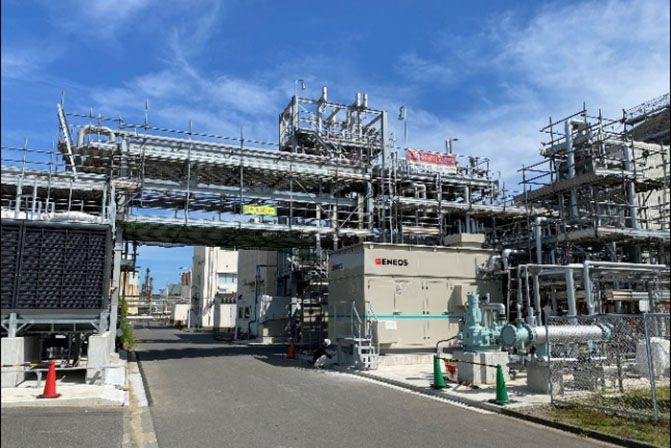
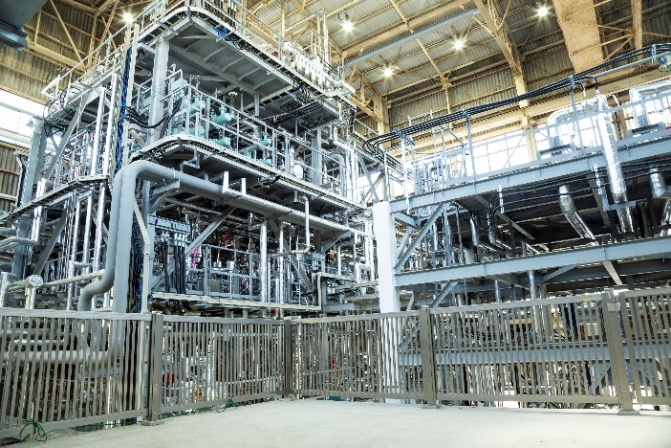
Following a roadmap framed by the Japanese government, the ENEOS group has been working on the development toward the commercialization of synthetic fuels, starting with beginning scale-up demonstrations in FY2022. In September 2024, the demonstration plant for synthetic fuel production commenced demonstration operations.
The fuels produced were used during the Expo 2025 Osaka, Kansai, Japan※1 event period in the shuttle buses (diesel oil) and other vehicles used to transport on-site guests and related parties (gasoline).(details).
Going forward, we aim for the realization of the widespread social adoption of environmentally friendly synthetic fuels through the development achievements from the Green Innovation Fund project in the near future.


※1 ©Expo 2025